Petroleum Products
Naphtha
Suppose you have a question to know what naphtha is. In that case, we must say that naphtha is one of the most important and widely used fractions of crude oil, and familiarity with the properties and uses of this petroleum fraction is necessary for a process engineer. This article will teach you what you need to know about naphtha.


What is Naphtha?
One of the essential intermediate products of the crude oil refining industry is naphtha. This product is used as feed in petrochemical units, including steam crackers, catalytic conversion, and isomerization. All kinds of naphtha cuts are produced and supplied in refinery processes.
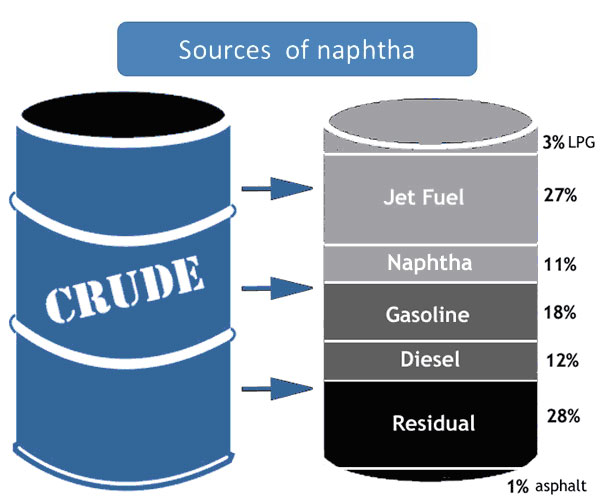
A naphtha is a group of liquid hydrocarbon compounds that are highly volatile and flammable. Naphtha is a general term and refers to the compounds between gas cuts and kerosene in crude oil distillation processes. These compounds make up about 11% of crude oil.
The central part of gas condensate, i.e., fat, collected from the gas well, is also composed of naphtha. This liquid fuel can also be extracted from coal tar. This category of compounds contains 5-12 carbon atoms, which generally include paraffin, olefins, naphthenic, and aromatics. Among these materials, aromatic compounds in naphtha cause a pungent smell that is also very harmful to humans.
Types of Naphtha
In general, naphtha is divided into two categories based on the number of carbon atoms in them, which are:
- Light Naphtha
They contain 5-6 carbon atoms that boil at 30-145 degrees Celsius.
- Heavy Naphtha
This category of naphthas contains 7-12 carbon atoms, and their boiling point is 140-200 degrees Celsius.
Each of these types of naphthas has different uses in different industries.
Naphtha production methods
Naphtha can be produced by several methods, which include:
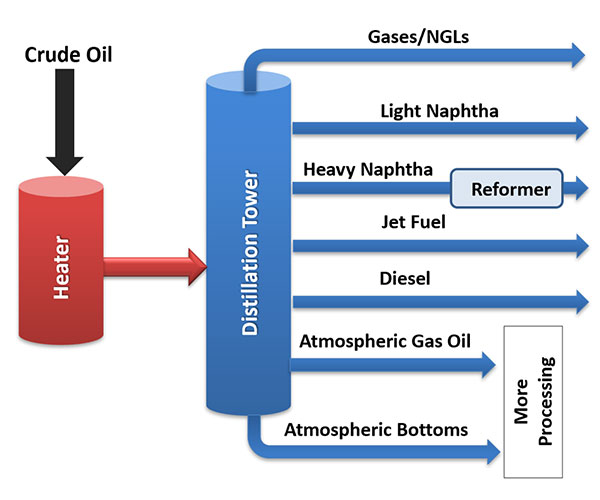
- Distillation of crude oil
- Solvent extraction
- Hydrogenation of crude oil distillates
- Polymerization of unsaturated hydrocarbon compounds such as olefin
- Alkylation process
The most important and common method of their production is crude oil distillation.
Application of Naphtha
Naphtha has various uses. The Chemical and petrochemical industries are the primary buyers of naphtha, Which is used as a feed for the production of different petrochemical products, including solvents and diluents, raw materials for all types of plastics, synthetic fibers, and industrial alcohols. For example, the majority of dye thinners consist of naphtha. And most ethylene plastic compounds are made with naphtha.
Also, using catalytic processes, naphtha can be converted into high-octane gasoline and other petroleum fuels. Naphtha is a potent solvent with various applications. For this reason, it is also used to produce detergents and purify other hydrocarbon substances. It is also used to make polishes and varnishes and as heating and cooking fuel (similar to LPG and kerosene).
Characteristics
- Odor: In general, paraffin compounds have the least, and aromatic compounds have the most pungent odor; the smell of naphtha, which is a mixture of various compounds, depends on the amount of each of these substances.
- Color: Naphtha is colorless in general, but it may show pale yellow in the presence of a high amount of aromatic compounds.
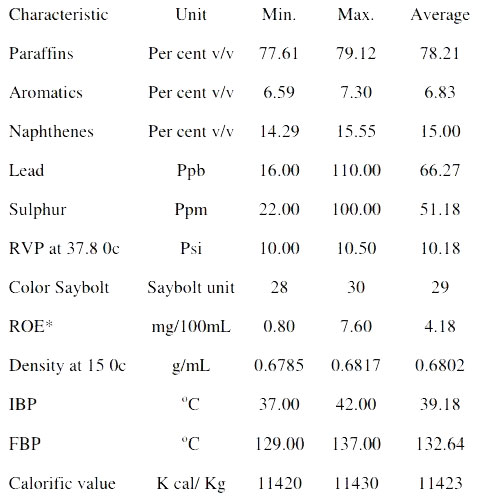
In the figure below, the specifications of light naphtha can be seen:
Converting naphtha to gasoline with catalytic reforming
Catalytic reforming of naphtha is one of the basic operations in oil refining and petrochemical industries, which is widely used to convert low octane hydrocarbons into high octane gasoline without changing the boiling range. Naphtha usually makes up 15 to 30 percent of crude oil weight and boils between 30 and 200 degrees Celsius. In addition, the products produced during the catalytic reforming process, such as benzene, toluene, and xylenes (BTX), are essential petrochemical compounds. Hydrogen is also produced as a side product during this process, which is one of the critical materials in many circles.
Naphtha is a complex combination of different hydrocarbons, and various reactions occur between these compounds, including dehydrogenation and dihydroisomerization of naphthenic to aromatics, dehydrogenation of paraffin to olefins, dihydrocyclization of kinds of paraffin and olefins to aromatics, isomerization and hydroisomerization to isoparaffins, isomerization of alkyl cyclopentane and hydrocracking of paraffin and naphthenic to lighter hydrocarbons.
Safety considerations
Considering that we understand what naphtha is and what its uses are, we should pay attention to the fact that naphtha. At the same time, it is a very widely used and susceptible substance. The industries that produce it should take into account the necessary measures for the safety of employees. The contact of naphtha with human skin causes irritation, swelling, and pain in that area. If a person is in the vicinity of naphtha compounds for a long time, he may suffer from respiratory or mental problems. Also, as mentioned at the beginning, these materials are very volatile and flammable, so in the design of the process, these safety considerations should also be taken into account.
Naphtha and petrochemicals
As mentioned, naphtha is one of the essential feedstocks used in the petrochemical industry. Naphtha in crude oil refineries is usually fed to gasoline units (Catalytic Reforming) and isomerization to produce reformate (Reformate) and isomerate (Isomerate) in the gasoline pool, mixed, and supplied as fuel. It should also be noted that petrochemical complexes produce light olefins (ethylene, propylene, butadiene, and butylenes) and aromatics (benzene, toluene, and xylene) that the feed of these units is light and heavy naphtha.
Currently, nine refining complexes in Iran and two refineries under construction, such as Persian Gulf Star and Siraf, have the potential to supply naphtha. It is worth mentioning that many gas and liquid gas (NGL) units in the country also produce and provide light and heavy naphtha.
Due to access to light and quality hydrocarbon resources such as gas liquids (NGL), condensate, and light crude oil, Iran can produce quality and competitive naphtha to provide to the petrochemical industry with the help of processes Cracker with steam and aromatic production to create essential products and develop the value chain of these products.
We at Iran Petroleum are by your side to supply the highest quality and rarest Iranian Petroleum Products. Our professional consultants will accompany you in this way.











Leave a Reply